Choosing the right window glazing is one of the most important decisions a New Zealand homeowner can make. From reducing heat loss to minimising outside noise, the type of glazing you choose will impact your home’s comfort, energy efficiency, and long-term costs.
In this guide, we’ll break down the key window glazing types available, including single, double, and triple glazing. We’ll also explore the types of glass used and what glazing options work best for New Zealand’s climate.
Our glass thickness and laminated panes act as a shield, significantly reducing external noise. Enjoy peace and tranquillity, undisturbed by the chaos outside.
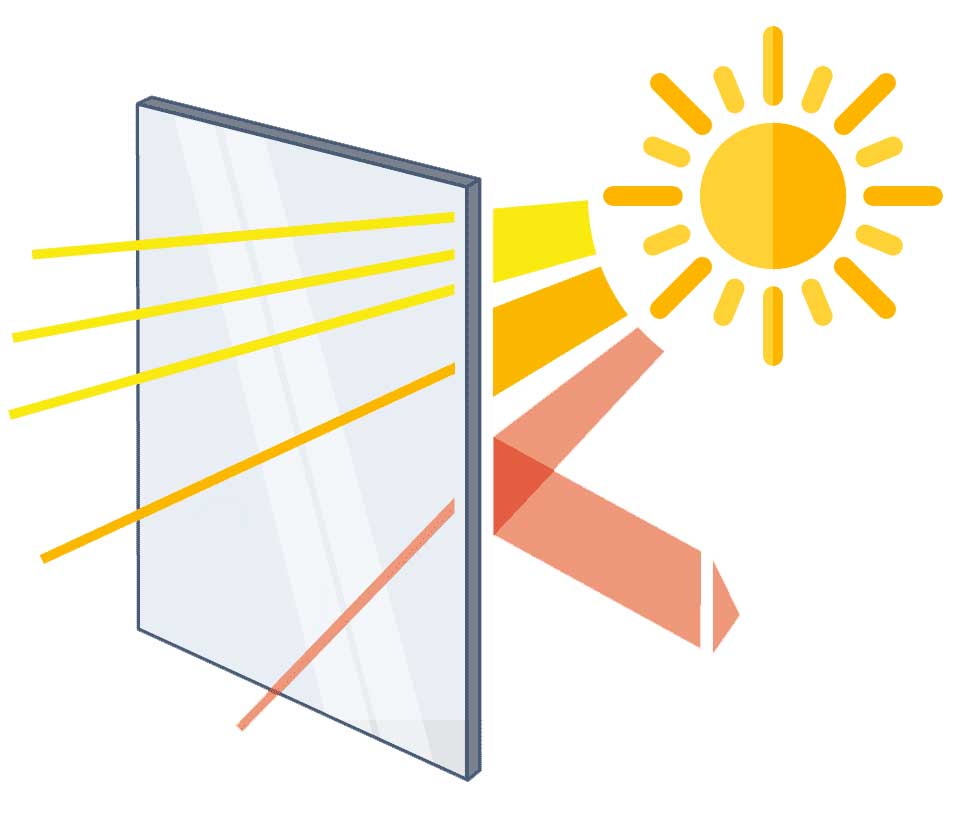
New Zealand's sun can be harsh, but your furnishings needn't suffer. Our laminated glass and tinted glass options shield your interiors against the relentless New Zealand sun.
Safety is non-negotiable. Our clever use of glass thickness and laminates goes beyond aesthetics; it's a robust security feature. Ensure the safety of your loved ones and the sanctity of your space.
Your home, your rules. Our obscured glass and tints offer a spectrum of privacy options. Tailor the intimacy of your spaces to your liking, with glass solutions that respect your need for seclusion.
Every piece of glass reflects quality, craftsmanship, and innovation. With Veridian Glass’ expertise and our commitment to excellence, we present you with glass options that surpass expectations.
Our glass options enable you to elevate thermal insulation to unprecedented levels. Feel the warmth in winter, embrace the coolness in summer – it's a year-round comfort revolution.
Window glazing refers to the glass fitted within a window frame. While the term can describe any pane of glass, it’s commonly used when discussing energy performance and insulation.
Glazing plays a critical role in keeping homes warm in winter and cool in summer. It also affects soundproofing, UV protection, and even safety.
When choosing glazing options in NZ, consider:
Many NZ suppliers offer glazing tailored to local conditions. Look for products with low U-values (lower heat loss).
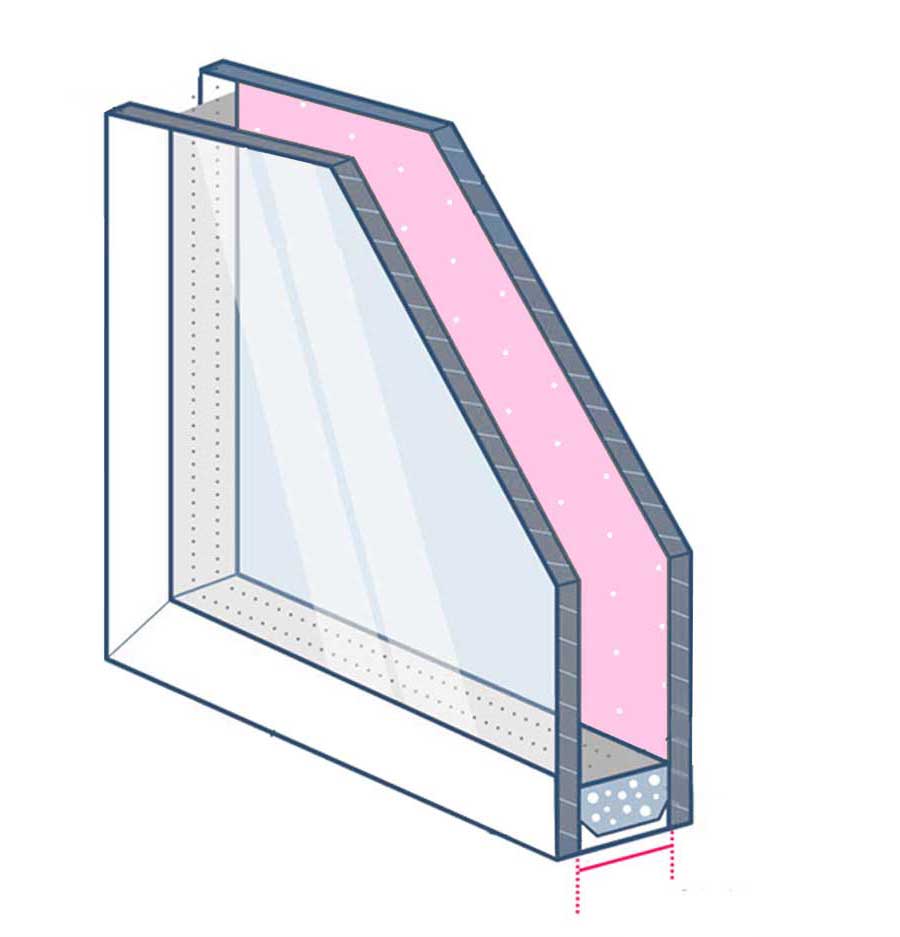
Double glazing consists of two panes of glass separated by a spacer. The gap between the panes is often filled with air or argon gas to improve insulation and noise reduction.
Benefits:
Double glazing is the most common choice for New Zealand homes, offering a good balance between performance and cost.
Triple glazing uses three panes of glass, with two air or argon gas-filled gaps in between. It’s designed to offer maximum energy efficiency.
Advantages:
Considerations:
While triple glazing offers the best thermal performance, it is not always necessary for every New Zealand home. We recommend triple glazing as a more practical choice for homes in the colder regions of New Zealand.
We’re not just meeting standards; we’re surpassing them. Our standard double-glazed units not only comply with NZ Building Code requirements but go beyond, boasting an impressive thermal resistance rating of R 0.40/U 2.51.
You could also choose windows that include both argon and high-performance Low E. This creates an outstanding thermal resistance rating of R0.77/U1.3, outperforming any thermally broken aluminium joinery in the market.
For those seeking maximum efficiency, our triple-glazed panels boast an extraordinary R (window) Value of R 1.20/U 0.83, ensuring unparalleled thermal insulation and comfort.
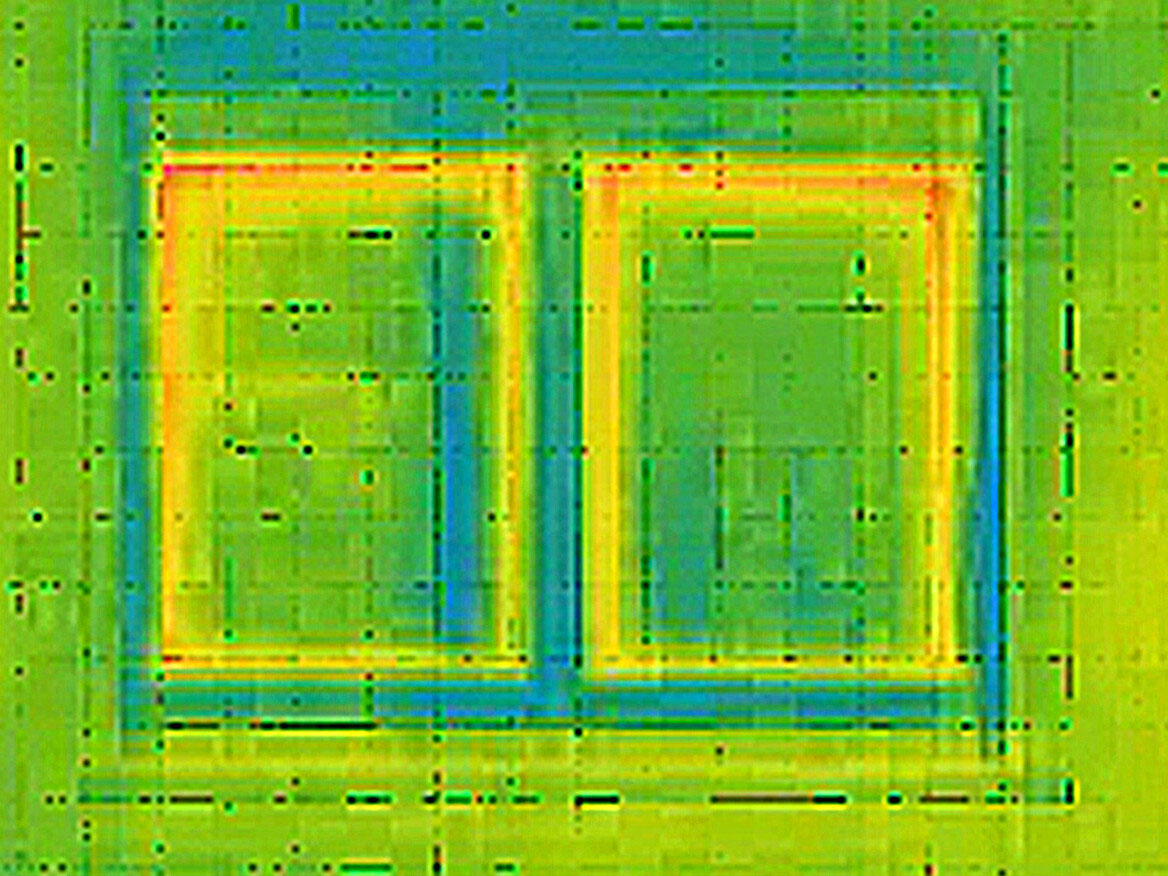
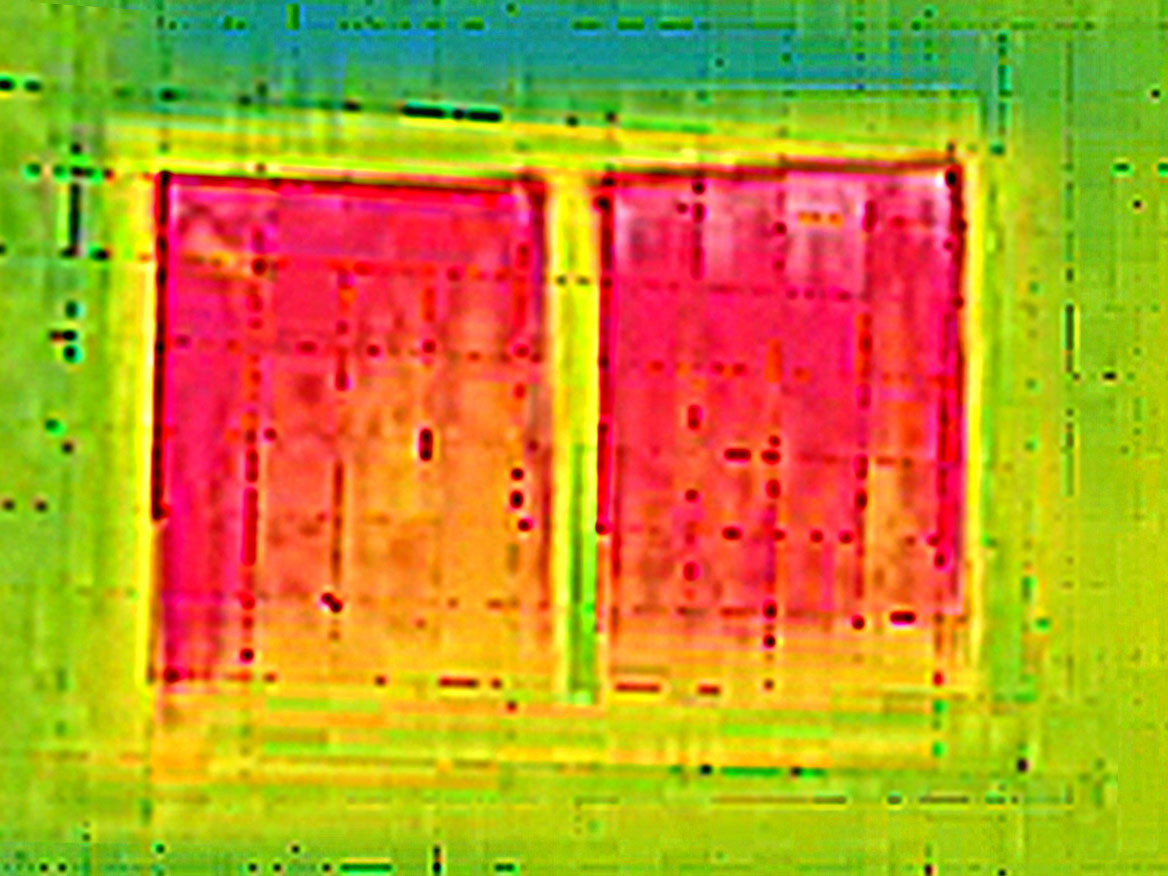
The above image was taken using a thermal imaging camera to illustrate the thermal resistance of our standard double-glazed units. The first image shows the window mostly red, indicating heat loss. You can move the slider to the right to see the window with double glazing, the green and blue colours indicating far less heat loss.
The glass used in glazing units affects how well windows perform. Here are some common types:
Low-E Glass (Low Emissivity)
Low-E glass is our most popular glazing option. For a small investment, the addition of a Low-E coating can more than double the thermal performance of the glass, offering significant long-term savings on your energy bills.
Laminated Glass
Toughened (Tempered) Glass
It’s important to note that for certain applications, such as doors, low windows, and bathrooms, the New Zealand Building Code legally requires the use of tempered glass.
Obscure glass is a great option for privacy without losing natural light. It blurs the view from outside but still lets daylight fill the room, making it ideal for bathrooms or street-facing windows. In addition to being practical, it adds a clean, modern touch to any space.





Under the latest New Zealand Building Code (Clause H1), all new homes and major renovations now require high-performance window and door glazing. The code sets minimum thermal resistance (R-value) requirements based on your home’s location within New Zealand’s six climate zones.
Choosing glazing that significantly exceeds these minimums is the best way to ensure genuine comfort and long-term energy savings. Our products are designed to do just that:
In New Zealand, a window’s performance is measured by its R-value (thermal resistance). A higher R-value means better insulation and a warmer home.
You may also see a U-value (thermal loss), which is common in international standards. For U-values, a lower number is better. The two are simply inverses (R=1/U).
At NK Windows, we use technologies like Low-E glass and argon gas to achieve exceptionally high R-values, maximising your home’s warmth and energy efficiency.
At NK Windows, achieving low U-values involves a combination of technologies. We utilize Low-E glass and Solar Control Glass to minimize heat loss. Additionally, our windows feature argon gas instead of air between the glass panes and incorporate warm edge spacer bars for enhanced thermal efficiency. The slim-profile frame, composed of a five-chamber profile frame and a six-chamber profile sash, further reduces heat conductivity.
Your glazing choice depends on your climate, budget, and comfort goals.
Upgrading your windows can transform your home’s comfort and performance year-round.
Our passion for creating homes filled with warmth and comfort extends to every detail. We keep it real, and when we understand your priorities, we can give you a variety of choices without overwhelming you with unnecessary options.
Visit our showroom and see our wide collection of samples to give you a real sense of how we will enhance your living spaces.
Double, and triple glazing are the main options. Each has different thermal and acoustic benefits.
Double glazing uses two panes of glass with a gas or air-filled gap in between for better insulation.
Triple glazing includes three panes of glass and two insulating gaps. It’s best for colder regions.
Common options include Low-E, laminated, toughened, tinted and obscure glass, each offering specific benefits.
Consider your climate, budget, and home orientation. Double glazing suits most homes, while triple glazing is best for colder regions.
High-quality window glazing, like the uPVC double or triple glazing offered by NK Windows, can last 20–30 years or more with proper maintenance. The lifespan depends on the glass type, frame quality, and exposure to harsh weather conditions.
Low-E (Low Emissivity) glass has a microscopic coating that reflects infrared heat while allowing visible light to pass through. This keeps your home warmer in winter by trapping heat inside and cooler in summer by reflecting external heat, improving energy efficiency.
Yes, certain glass types, like Low-E and tinted glass, block a significant portion of UV rays, protecting furniture, flooring, and interiors from fading. This is especially useful for north-facing windows with high sun exposure.
Need expert glazing advice for your home? Contact a local window specialist to explore double and triple glazing options suited to your region and budget.